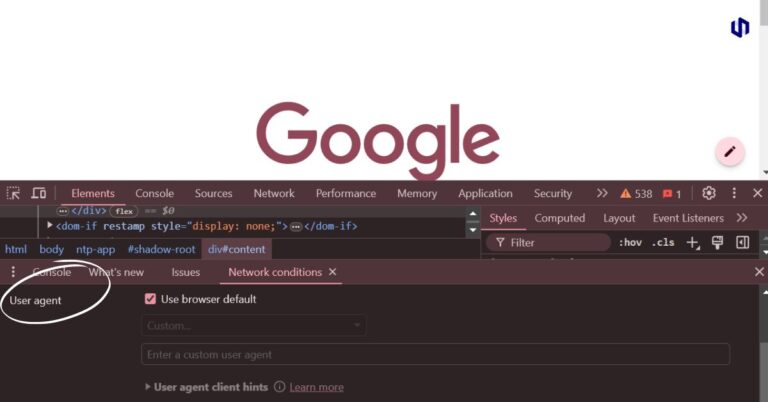
Understanding User Agent Spoofing: A Comprehensive Guide
This blog aims to unravel the intricacies of user agent spoofing, exploring its mechanisms, implications, and best practices to mitigate its effects. Whether you are a seasoned marketer or a tech enthusiast, this detailed guide will provide valuable insights into this increasingly relevant topic.